
Did you know? The Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) process can remove up to 90% of suspended solids in municipal water treatment—redefining industry standards for clean water. With water quality challenges on the rise, modern solutions like the DAF process are not just beneficial—they’re essential for industrial and municipal water treatment success. Whether you’re seeking to optimize a treatment plant or ensure safe drinking water, understanding how DAF works will put you ahead of the curve.
Revealing the Untold Impact of the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) Process in Water Treatment
The Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) process stands at the forefront of cutting-edge water treatment technology, efficiently addressing the toughest contaminants in today’s water streams. By leveraging the power of microbubbles , DAF units consistently outperform traditional sedimentation and clarification methods. Imagine having the ability to remove oils, grease, and even the smallest suspended solids with precision—and all at an impressive throughput. In both municipal and industrial settings, adopting the DAF process is about more than compliance: it’s about redefining water quality, protecting the environment, and supporting robust public health initiatives.
From reducing organic contaminants to ensuring wastewater treatment plants meet stringent regulations, the DAF process delivers reliability, cost-savings, and sustainability. Results are immediate: clearer water, less sludge, and a dramatic drop in hazardous pollutants. If you’ve yet to explore the lasting benefits of the DAF system, now is the time—today’s environmental challenges demand the science and scalability DAF brings to every water treatment process .
Understand what the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) process is and how it works
Explore key benefits of the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) process for water and wastewater treatment
Learn about DAF units, DAF systems, and key operational considerations such as flow rate and suspended solids removal
Examine how the DAF process compares to alternative air flotation technologies
Discover real-world industrial and municipal applications of dissolved air flotation
Get answers to the most frequently asked questions on the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) process
"Did you know? The Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) process can remove up to 90% of suspended solids in municipal water treatment—redefining industry standards for clean water."
How the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) Process Works: A Deep Dive Into Air Flotation Principles
Understanding the dissolved air flotation (DAF) process starts with the simple principle of density manipulation: leveraging tiny bubbles of pressurized air to separate contaminants from water. In practical terms, the DAF system injects pressurized air into a recycled water stream, creating millions of microbubbles that attach to suspended particles, fats, oils, and grease. As these bubbles float upward, they force contaminants to rise to the surface of the water, forming a layer of sludge ready to be removed by a skimming device . This stage is crucial for achieving a highly clarified effluent with minimal chemical input compared to alternative processes.
But what about handling fluctuating contaminant loads or changing flow rates? DAF systems are engineered to accommodate variability by adjusting dissolved air delivery and optimizing the air to solids contact time. With customizable flow rates and robust tank design, a DAF unit can seamlessly integrate into new or retrofitted water treatment plants. The outcome: consistently superior removal of suspended solids and organic matter, making DAF a preferred treatment process for complex water and wastewater treatment challenges.
Step-by-Step Mechanics of the DAF Process: Dissolved Air and Water Separation
Introduction to pressurization and release of dissolved air
The role of microbubbles in separating suspended solids
Clarification of the water stream and collection of floating sludge
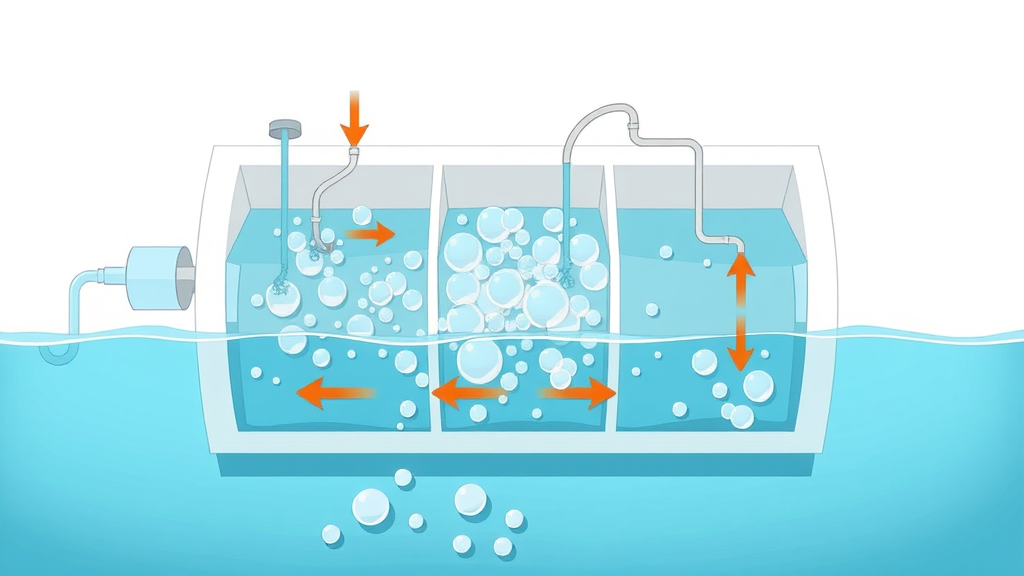
The DAF process begins by saturating a portion of the clean water output with compressed air under high pressure in a separate, dedicated tank. This pressurized mixture is then injected back into the main flotation tank , where sudden release to atmospheric pressure allows dissolved air to come out of solution, forming millions of air bubbles just microns in size. These tiny bubbles are essential; as they travel through the incoming water stream , they quickly adhere to suspended solids , oils, and grease. The buoyant force causes these contaminants to rise to the surface of the water—hence the term "air flotation."
Once at the top, the resulting sludge blanket is systematically removed by a skimming device (mechanical or hydraulic). Beneath, the clarified water is collected as effluent, ready for additional treatment or discharge. The integration of pressurized air and microbubble technology is what distinguishes DAF from simpler sedimentation: the efficiency of lifting even fine particles, and the reliability in varying water or wastewater conditions.
Key Components of a DAF Unit: From Inlet Chamber to Sludge Hopper
DAF tank design and flow rates
Mixing zone: optimizing air to solids contact
Surface scraper and collection mechanisms
A well-designed DAF unit contains several critical parts, starting with the inlet chamber —where influent water is evenly distributed and gently introduced into the system. The real efficiency gains come next: in the mixing zone , dissolved air combines vigorously with influent to maximize contact between microbubbles and contaminants. Careful control of velocity and turbulence ensures efficient collisions without breaking up flocs .
The treated water flows through the main tank where microbubbles attach to solids, lifting them to the top. At the surface, a skimming device or surface scraper moves the thickened layer of sludge into a collection hopper. Below the flotation zone, a series of baffles guide the clarified water toward discharge, while heavy grit may settle and be removed separately. The tank’s overall design and flow rate flexibility make modern DAF systems adaptable to everything from small portable setups to massive municipal installations.
Comparison of DAF System Components and Functions | ||
Component |
Function |
Contribution to DAF Process |
|---|---|---|
Inlet Chamber |
Distributes influent water evenly |
Reduces turbulence, improves particle-bubble contact |
Pressurization System |
Saturates recirculated water with dissolved air |
Ensures a robust supply of microbubbles |
Mixing Zone |
Merges air-saturated water with influent |
Maximizes solid-bubble adherence, boosts separation |
Flotation Tank |
Allows particles to float to the water surface |
Provides retention time, ensures effective clarification |
Surface Scraper |
Mechanically removes floating sludge |
Continuous solids removal, prevents recontamination |
Sludge Hopper |
Holds collected sludge before handling/disposal |
Enables easy, hygienic waste management |
Effluent Collection |
Channels clarified water for reuse or discharge |
Delivers high-quality effluent ready for downstream processes |
Critical Applications of the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) Process in Wastewater Treatment
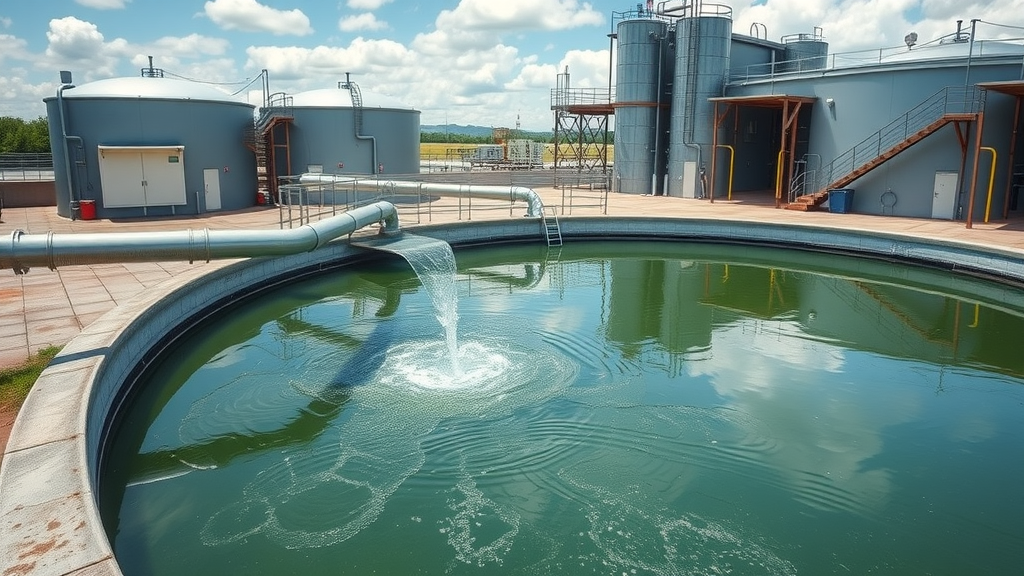

The dissolved air flotation (DAF) process has redefined the landscape of wastewater treatment by providing unparalleled efficiency in the removal of persistent contaminants. In industrial settings, DAF systems tackle complex waste streams laden with oils, fats, and heavy organic loads—common in food processing, petrochemical, and pulp and paper plants. By removing these compounds early in the treatment process, facilities not only reduce chemical consumption but also prolong the service life of downstream systems and minimize environmental impact.
With municipal water utilities, DAF delivers a powerful pre-treatment solution for drinking water plants and secondary clarification. Municipal DAF installations can easily handle fluctuating flows and rising contaminant loads due to population growth or industrial discharge surges. The logic is simple: by lifting and isolating contaminants at the very start, the entire treatment system performs better, with improved reliability and lower operational costs. Successful case studies demonstrate how DAF technology has revolutionized industrial wastewater re-use projects and advanced public health protection worldwide.
Wastewater Treatment: Harnessing the Power of DAF Systems for Industrial and Municipal Use
Addressing challenging industrial waste including oil and grease removal
Municipal wastewater treatment advances: from pre-treatment to effluent polishing
Case studies: DAF process efficiency for drinking water and industrial wastewater projects
Industrial operations such as meat processing and oil refineries face stubborn challenges—oily residues, emulsified fats, and difficult-to-settle suspended matter . Here, DAF units shine by using tiny bubbles to agglomerate and float these impurities, whereas conventional sedimentation would fail. By removing these substances with a DAF system , plants prevent downstream clogs, lower chemical dosing, and drastically reduce sludge hauling costs. In municipal plants, DAF optimizes both pre-treatment (as a buffer to protect biological processes) and post-treatment (polishing effluent to ultra-low turbidity), securing consistently high drinking water quality.
Case studies across North America and Europe have spotlighted impressive metrics: over 90% suspended solids removal, 80% oils and grease elimination, and compliance with even the strictest discharge limits. These real-world results demonstrate that DAF is not a luxury—it's a necessity for modern, resilient wastewater treatment .
Suspended Solids and Turbidity: Optimizing DAF for Complex Water Streams
Managing variability in suspended solids concentration
Adapting DAF systems for fluctuating flow rates and quality assurance
In environments where suspended solids and turbidity levels fluctuate, a well-designed DAF system adapts in real-time to ensure compliance. Rapid industrial discharge, rain events, or accidental contamination require flexible treatment. Operators routinely adjust flow rates and chemical dosages, fine-tuning the daf unit for optimal performance regardless of changing influent quality. The process involves careful monitoring of incoming water stream parameters and modulating dissolved air saturation for maximum efficiency.
Advanced automation now makes it possible to handle variable water chemistry and solid concentrations without operator intervention. With remote sensors and AI-driven analytics, DAF systems can proactively adapt, maintain target suspended solids removal, and consistently produce clarified water .
DAF Systems Design: Customizing the Dissolved Air Flotation Process for Diverse Applications
DAF Unit Sizing and Flow Rate Considerations in Water Treatment Plants
Calculating optimal flow rates for treatment efficiency
Scalable DAF systems: portable vs. fixed installations

Choosing the right DAF system begins with accurately predicting your plant’s operational flow rate —the volume of water stream requiring treatment each day. Underestimating flow rates may result in system overloads, while overestimating can lead to overspending and underutilization. A typical daf unit is designed for specific influent loads, throughput, and removal targets. Engineers take into account peak, average, and future projected flows as well as the composition of suspended matter to size tanks, pumps, and air-saturation systems for continuous efficiency.
Facilities with space constraints or evolving needs can opt for modular, portable DAF solutions that scale as requirements change. Fixed installations favor high-volume centralized facilities, while portable DAFs support on-demand, decentralized, and pilot applications in remote locations. Both configurations deliver cost-effective, reliable dissolved air flotation regardless of project size.
Integration of DAF Process with Existing Water Treatment Systems
Supplementing conventional clarification and filtration processes
Hybrid DAF systems for enhanced contaminant removal
While a DAF system operates as a robust standalone solution, its greatest potential emerges when integrated into multi-stage water treatment architectures. In older plants, retrofitting DAF units as pre-clarifiers protects sensitive biological treatment stages and enhances filtration lifespan. Hybrid setups that combine DAF with advanced oxidation or membrane filtration yield drinking water and industrial effluent with next-level purity, even from sources historically deemed too challenging to treat.
Integration is seamless—DAF units can operate at different points within the treatment process , providing redundancy, emergency bypass, or specialty polishing on demand. This flexibility allows operators to adapt to emergencies, regulatory changes, and process innovations without large-scale infrastructure overhaul.
Comparing Dissolved Air Flotation vs. Other Air Flotation Methods

Dissolved Air Flotation vs. Suspended Air Flotation (SAF): What Sets Them Apart?
To select the right air flotation process, it’s essential to compare the leading alternatives— Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) and Suspended Air Flotation (SAF) . While both techniques employ air bubbles to separate suspended solids from the water stream , their mechanisms and performance diverge sharply. In DAF, air is dissolved into water under high pressure, forming microbubbles when pressure is released. These microbubbles are exceptionally effective at binding with tiny, lightweight contaminants and lifting them to the surface.
In contrast, Suspended Air Flotation (SAF) systems inject air into water without pressurization. The resulting bubbles are typically larger—less effective at capturing fine particles and may require longer retention in the flotation tank . For fine suspended solids and oily contaminants common in industrial wastewater , DAF units deliver faster, more efficient removal. SAF systems, by offering simplicity and ease of operation, may suffice for less rigorous needs.
Comparison Table: DAF vs. SAF in Wastewater Treatment Performance | ||
Parameter |
DAF |
SAF |
|---|---|---|
Air Bubble Size |
Small (20-50 micron microbubbles) |
Larger (100-300 micron bubbles) |
Pressurization |
Requires high-pressure saturation |
Works at atmospheric pressure |
Particle Removal Efficiency |
Very high, even for fine particles |
Lower for fine particles, better for larger solids |
System Complexity |
Moderate to advanced |
Simpler, fewer components |
Scalability |
Highly scalable for industrial/municipal |
Suited for small to mid-sized plants |
Typical Applications |
Municipal, industrial, oily wastewater |
Small-scale solids, low-complexity waste |
Efficiency, Cost, and Scalability: Making the Right Air Flotation Choice
In evaluating air flotation methods, it’s clear that the DAF process is unmatched in efficiency when the goal is to remove high concentrations of suspended solids , oils, or greases, particularly in challenging industrial waste or hazardous municipal streams. DAF units achieve higher throughput with less footprint than SAF, translating into better ROI for large-scale operations. That said, SAF systems may provide a cost-effective, easy-to-operate solution for facilities processing mostly coarse material, with limited space or budget for advanced pressurization systems.
Scalability is another deciding factor. DAF’s modularity and automation make it adaptable for both small startups and massive municipal installations. Over time, facility managers should assess contaminant levels, regulatory requirements, and future expansion plans to inform their selection.
"DAF units deliver superior removal of fine particles, setting a higher standard in water treatment than traditional sedimentation methods."
Essential Factors Influencing the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) Process Outcome
Flow Rate, Water Chemistry, and Dosage: Mastering DAF Process Optimization
Fine-tuning coagulant and flocculant dosages
Controlling dissolved air saturation for improved separation
Continuous monitoring to handle variable water streams

Process optimization in DAF hinges on striking the right balance between flow rate , chemical dosing, and air saturation. Operators closely monitor influent water for organic loads, solids content, and pH to adjust coagulant and flocculant dosages—chemicals that encourage particles to clump together and anchor microbubbles . Too little coagulant, and floating solids may slip through; too much, and sludge volumes spike, raising costs. By fine-tuning air saturation and release pressure, DAF operators ensure milliions of air bubbles bind quickly and efficiently to contaminants.
Smart sensors tracking real-time water chemistry and flow enable automated process adjustments to accommodate unexpected changes—a critical advantage for industrial applications facing variable waste loads. The combination of advanced process controls and robust equipment means even municipal plants dealing with seasonal change or storm surges sustain consistent, compliant output from their DAF units.
Maintenance Best Practices for Long-Term DAF System Performance
Routine cleaning and component checks
Upgrading control systems for predictive maintenance

Long-term excellence from any DAF system depends on diligent maintenance. Routine checks on pressurization systems , mixing chambers , and moving parts such as surface scrapers (skimmers) prevent breakdowns and keep air bubble formation and solids removal at optimum levels. Cleaning tanks, desludging the sludge hopper , and removing buildup ensures process consistency and high effluent quality.
Modern DAF installations leverage advanced control systems with predictive analytics—prompting maintenance on pumps, sensors, and dosing units before performance drops. Training staff on routine inspection, recordkeeping, and reaction to emergency signals ensures compliance and minimizes downtime, extending both equipment lifespan and treatment system performance.
Top Benefits and ROI of Employing the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) Process in Industrial Waste and Water Treatment
Significant reduction in suspended solids and organic contaminants
Reduced chemical consumption and sludge volume
Enhanced compliance with wastewater discharge regulations
Improved clarity and safety of drinking water

The business case for deploying the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) process is powerful and measurable. Not only do DAF units achieve up to 90% removal efficiency for suspended solids , oils, and grease, but chemically assisted systems reduce the need for additional coagulants and flocculants, lowering ongoing reagent costs. Smaller sludge volumes translate directly into less frequent handling, safer operations, and reduced disposal fees—major cost drivers for large and small plants alike.
Crucially, by exceeding wastewater treatment and drinking water quality regulations, companies and utilities avoid fines, reputational risk, and public health crises. For industrial sites, DAF improves water recycling potential and environmental stewardship, while in municipalities, it ensures consistently clear, safe tap water—key for thriving communities and businesses. The Return on Investment (ROI) in DAF is not only faster than many alternative systems but continually improves as regulations tighten and societal demand for sustainability grows.
Answering Common Questions about the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) Process
What is the process of dissolved air flotation?
The dissolved air flotation (DAF) process is a water treatment method that clarifies wastewater by removing suspended solids, oils, and other contaminants through the introduction of dissolved air, creating microbubbles that lift impurities to the surface for removal.
What is dissolved air flotation DAF for wastewater treatment?
DAF for wastewater treatment is a proven technique in both municipal and industrial contexts, utilizing dissolved air to separate pollutants from water for safer disposal or reuse.
What does DAF stand for in wastewater?
DAF stands for 'Dissolved Air Flotation,' reflecting the process’s reliance on air dissolved into water to aid in contaminant removal.
What is the difference between DAF and SAF?
Whereas Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) introduces and releases air into water under pressure to form microbubbles, Suspended Air Flotation (SAF) incorporates air without pressure, resulting in different removal efficiencies and system designs.
What are the critical design considerations for a DAF system? Selection of flow rate performance, tank sizing, air saturation methods, and solids loading are critical in custom DAF design for maximum efficiency and reliability.
How does temperature affect DAF process efficiency? Higher temperatures typically enhance air solubility and bubble formation, but extreme cold or heat may reduce flotation efficiency or impact chemical reaction rates in the process.
Which industries benefit most from using the dissolved air flotation (DAF) process? DAF is widely deployed in oil & gas, food processing, textile, pulp and paper, and municipal water treatment, wherever rapid, high-efficiency removal of suspended solids and oils is needed.
The Future of the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) Process: Innovation, Sustainability, and Safer Water
"The evolution of dissolved air flotation is key to meeting the world's increasing demand for sustainable water solutions."

The future of the dissolved air flotation (DAF) process is being shaped by automation, remote monitoring, and green energy integration—tools that enable more sustainable, resilient, and transparent water treatment worldwide. As urbanization intensifies and environmental standards rise, DAF’s modularity and scalability make it indispensable for new smart cities, eco-districts, and emerging markets. Today’s investments in advanced DAF systems are tomorrow’s foundation for cleaner rivers, safer communities, and a sustainable global water supply.
Ready to Upgrade Your Water Treatment? Maximize Results with the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) Process Today
Get Our Free Evaluation – CALL US (626)-332-2500 – EMAIL US info@csi-environmental.net
Transform your water treatment process with the latest in dissolved air flotation technology.
Take action now : Contact our team for a custom assessment and discover how the DAF process can revolutionize your plant’s performance, reduce costs, and unlock new levels of environmental stewardship.
Upgrade your water treatment results—adopt the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) process for cleaner, safer, and more sustainable water solutions.
Sources
EPA – https://www.epa.gov/water-research/dissolved-air-flotation
Water Today – https://www.watertoday.org/sectiondissolvedairflotation.html
The article provides a comprehensive overview of the Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) process, highlighting its significance in modern water treatment. For further reading, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) offers an in-depth resource titled “Dissolved Air Flotation,” which delves into the technical aspects and applications of DAF systems. Additionally, Water Tech Online’s article “Understanding Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF)” provides practical insights into the operational benefits and considerations of implementing DAF technology. These resources will enhance your understanding of DAF systems and their role in effective water treatment.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment