
Did you know that Los Angeles County treats over 50 million gallons of industrial wastewater every single day ? Most people don’t realize how complex—and vital—the process is for both the environment and industry in cities like Diamond Bar. If you want to learn how advanced water treatment keeps businesses running and communities safe, you’re about to dive deep into the secrets behind these essential systems!
Staggering Facts: The Impact of Industrial Waste Water Treatment in Diamond Bar
Did you know? Over 50 million gallons of industrial wastewater are treated daily in Los Angeles County, setting standards for sustainable industrial practices.
Why Industrial Waste Water Treatment Diamond Bar Matters for Local Industry and Environment
Industrial waste water treatment in Diamond Bar isn’t just a regulatory checkbox—it’s a lifeline for local industries and a shield for our natural resources. Every year, significant volumes of industrial waste pass through the city’s advanced treatment plants, ensuring that contaminants are removed before rejoining the sewer system or local waterways. Proper management of industrial waste means businesses can maintain operations without risking shutdowns due to non-compliance, while the surrounding environment is protected from harmful chemicals and pollutants. Local industries—from manufacturing to food processing—rely on modern treatment processes to keep their doors open, jobs intact, and output safe. At the same time, effective wastewater management helps keep Diamond Bar’s surface waters and public health standards among the highest in Los Angeles County.
Beyond simple waste disposal, industrial waste water treatment in Diamond Bar upholds public trust in the region’s infrastructure and supports economic growth. The city’s investments in water treatment plants, sewer system upgrades, and advanced monitoring technology demonstrate a forward-looking commitment to sustainable development. Every drop of treated water sent through the sanitation system is a win for both industry and the environment. When it comes to safeguarding surface waters, supporting economic viability, and ensuring regulatory compliance, Diamond Bar stands as a regional leader in effective industrial waste management.

Understanding Industrial Waste Water Treatment Diamond Bar: Essential Concepts
Definition of industrial waste water treatment Diamond Bar: Industrial waste water treatment refers to the specialized processes developed to remove pollutants, chemicals, and particulates from water discharged by factories and industrial plants in Diamond Bar. The main goal is to ensure this water meets strict environmental standards before it’s released to the sewer system or natural waterways.
Key components of a robust water treatment process: An effective system incorporates pre-treatment (removing solids), primary/secondary treatment (biological and chemical processing), advanced filtration, and continuous monitoring. Central stages include sedimentation tanks, aeration chambers, chemical dosing, and disinfection units, all designed for optimal contaminant reduction.
The connection between wastewater treatment and the sewer system in Diamond Bar: Treated industrial waste water often connects directly to the municipal sewer system, flowing from plants via sewer lines to centralized treatment facilities. This collaboration ensures that local water quality is protected at every stage, preventing untreated waste from reaching surface waters or underground reserves.
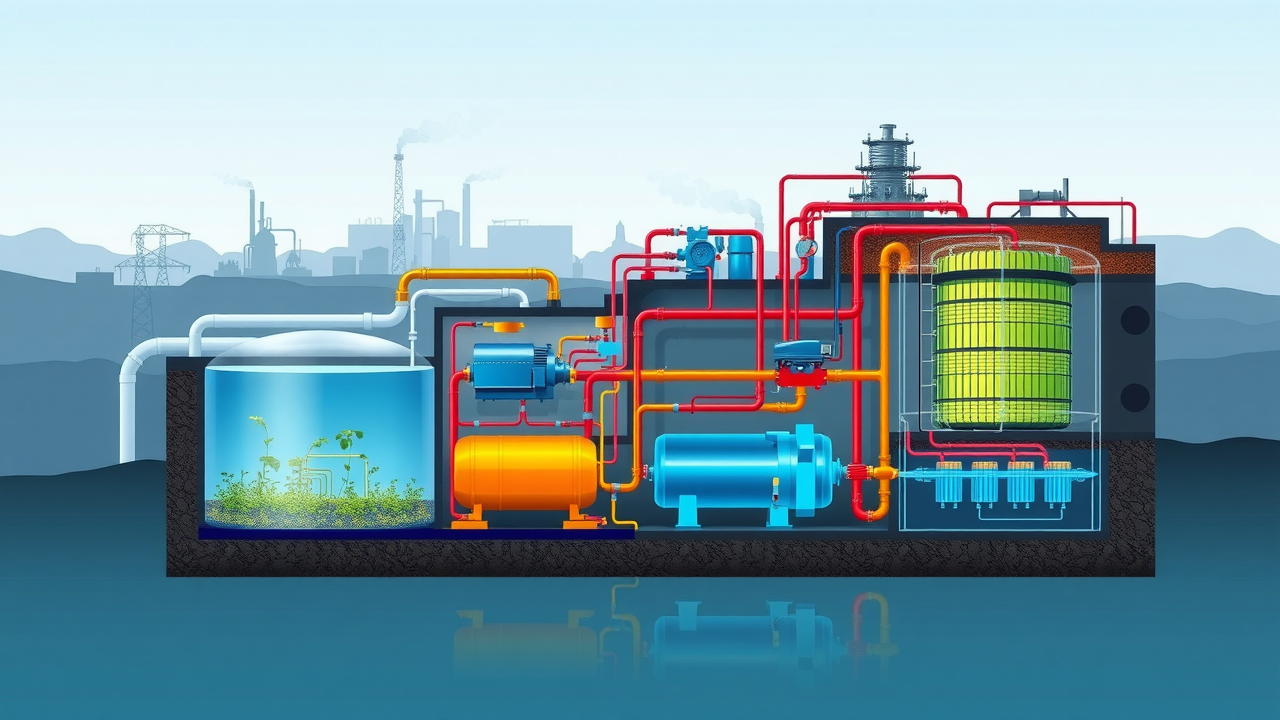
What You’ll Learn: Achieving Compliance and Sustainable Practices in Industrial Waste Water Treatment Diamond Bar
How Diamond Bar and Los Angeles County regulate industrial waste: You will discover specific regulations, permit processes, and enforcement bodies that govern industrial wastewater treatment—and why adherence is critical for every facility.
Types of treatment plants employed for wastewater treatment: Learn about centralized, decentralized, and on-site treatment plant options, and their roles in Diamond Bar’s infrastructure.
Steps to secure a waste disposal permit and remain compliant: Get insights into application processes, paperwork, and compliance milestones for securing an industrial waste disposal permit.
Advanced strategies for waste disposal and public sewer management: Uncover the latest technologies and practices for optimizing waste disposal and integrating with Diamond Bar’s public sewer system for maximum efficiency and safety.
The History and Evolution of Wastewater Treatment in Diamond Bar and Los Angeles County
Major Milestones in Water Treatment Infrastructure
The journey of industrial waste water treatment in Diamond Bar began in the mid-20th century, when growing populations and expanding industries created new environmental challenges. Early treatment plants in Los Angeles County relied on basic physical filtration and limited chemical treatments. Over time, stricter regulations and advancements in technology prompted Diamond Bar to invest in state-of-the-art water treatment facilities. Major milestones include installing biological treatment systems in the 1970s, integrating advanced chemical dosing and automated controls in the 1990s, and building new decentralized plants in the last decade to tackle growing demand and chemical complexity.
Today, Diamond Bar’s infrastructure features some of the most modern systems in the region, utilizing automation, remote sensing, and advanced filtration techniques. These improvements not only extend the lifespan of local sewer systems but also set new standards for public works across Los Angeles County. By investing in infrastructure upgrades and rigorous inspection routines, Diamond Bar continues to lead the way in industrial waste treatment, ensuring cleaner surface waters and enhanced local resilience against potential pollution.
Role of Los Angeles and Diamond Bar in Industrial Waste Management Advancements
The partnership between Los Angeles County and Diamond Bar has been pivotal in shaping regional industrial waste management strategies. While Los Angeles provided legislative and regulatory frameworks, Diamond Bar pioneered the integration of decentralized treatment options and innovative monitoring systems. This collaboration enabled the seamless flow of treated industrial waste into the public sewer while minimizing environmental impacts and ensuring that disposal permit requirements are consistently met.
These joint efforts have established Diamond Bar as a model for balancing industrial expansion and water quality protection. By sharing best practices and state-of-the-art treatment plant designs, these communities promote responsible growth and protect vital resources for future generations.

Industrial Waste Water Treatment Diamond Bar Process: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Source Collection and Pre-Treatment: From Sewer Line to Treatment Plant
The journey of industrial waste water in Diamond Bar begins in factories and production facilities. Wastewater is directed through the facility’s internal drainage system, often connecting to the municipal sewer line. Pre-treatment at the facility site captures oils, heavy metals, and large solids, preventing them from entering the broader sewer system. Compliance with local regulations is monitored closely; improper pre-treatment could result in a permit violation, costly fines, or operational shutdowns.
After pre-treatment, wastewater travels underground to centralized treatment plants via the city’s network of pipes, known as the sanitary sewer system. This system plays a crucial role in protecting both public infrastructure and environmental water quality by ensuring that hazardous industrial waste does not enter Diamond Bar’s water bodies or affect public health.
Physical, Chemical, and Biological Phases of Water Treatment
Once at the treatment plant , effluent undergoes rigorous multi-stage processing. The physical phase removes suspended solids through sedimentation and filtration. In the chemical phase , advanced dosing techniques neutralize toxic compounds and promote coagulation, helping to separate dissolved metals or organics. The biological phase leverages beneficial bacteria and microbes that degrade organic pollutants, removing dangerous substances prior to discharge.
Diamond Bar’s main treatment facilities employ high-flow aeration tanks and ultrafiltration membranes for advanced contaminant removal, often exceeding state and national water quality benchmarks. By the end of the process, the treated water meets stringent standards before being directed to public sewer systems or, in rare cases, safely released to surface waters.
Final Disposal: Wastewater Treatment System Outputs
After treatment, water leaves the facility through carefully controlled channels and is either discharged into the public sewer system or routed for further use, such as reclaimed water for landscaping or industrial applications. Residual materials—sludge, settled solids, or concentrated brine—are managed in accordance with Los Angeles County waste disposal regulations, often through controlled landfill disposal or further on-site treatment.
Advanced monitoring systems track the quality and quantity of every output to ensure compliance with all permit requirements and regulations. These safeguards help prevent illegal discharge into underground or surface waters , maintaining regional environmental health and protecting local communities.
Step-By-Step Visual Walkthrough of an Industrial Waste Water Treatment Plant in Diamond Bar
Getting a Waste Disposal Permit in Diamond Bar: A Comprehensive Guide
Legal Requirements for a Waste Disposal Permit in Los Angeles County
Every industrial facility in Diamond Bar must obtain a valid waste disposal permit before discharging wastewater into the public sewer system or local water bodies. Los Angeles County sets forth strict criteria to be met, including pre-discharge water quality tests, site inspections, and documentation of industrial processes. Failing to hold an up-to-date industrial waste disposal permit can result in hefty fines, forced shutdowns, or legal action. The City Council and Public Works offices work closely to enforce these regulations, backing compliance with regular audits and random facility checks.
By meeting legal requirements through careful documentation and best practices, industries play a critical role in protecting the sewer line, surface water, and the broader Diamond Bar environment. Seeking guidance from local officials during the application process helps ensure a smooth experience and minimizes risk.
Application Process for Industrial Waste Disposal Permit
The permit application process typically begins with a pre-application meeting with Diamond Bar’s environmental compliance division, followed by the submission of detailed forms outlining projected wastewater volumes, treatment types, and proposed disposal methods. Applicants undergo a thorough review, often including site visits and water quality tests before the permit is issued.
Proactive planning and clear communication with the relevant city departments smooth out the process. Facilities are encouraged to use official resources, such as online checklists and compliance guides, to navigate documentation requirements efficiently and prevent permit violations that can disrupt business operations.
"Without a valid industrial waste disposal permit, facilities risk severe fines and legal action in Diamond Bar."

Types of Waste Water Treatment Plants in Diamond Bar and Their Capabilities
Centralized Vs Decentralized Treatment Plants
Centralized treatment plants are large, municipally operated facilities serving multiple businesses through the extensive public sewer. They handle high volumes and employ cutting-edge technologies for efficient, consistent results. In contrast, decentralized treatment plants are smaller systems, often privately or semi-privately operated, designed for individual businesses or small clusters in industrial zones. These are vital in remote locations or where rapid expansion outpaces public works infrastructure.
Both types are monitored rigorously to ensure compliance with disposal permit regulations and must adapt quickly to changes in wastewater quantity or quality. Diamond Bar’s mix of centralized and decentralized facilities provides industry with flexibility while maintaining high regional water quality standards.
Comparison of Industrial Waste Water Treatment Systems in Diamond Bar |
||||
System Type |
Capacity |
Scalability |
Compliance Ease |
Typical Users |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Centralized |
High (10,000+ GPD) |
Excellent |
High |
Large manufacturers |
Decentralized |
Medium (500-10,000 GPD) |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Industrial parks, small factories |
On-Site |
Low (<500 GPD) |
Low |
Challenging |
Isolated or specialized facilities |
Innovations in Treatment Technology: What Makes Diamond Bar Unique
Diamond Bar has become a leader in leveraging innovative treatment plant technology , including membrane bioreactors, UV disinfection, and real-time digital monitoring. Integration with the city’s public works data network allows for instant alerts if water quality slips out of compliance, reducing risks to the sewer system and streamlining the reporting process.
Recent investments in green technology—such as solar panels and energy-efficient pumps—further reduce the environmental footprint while keeping operational costs manageable for industries. These ongoing upgrades reinforce Diamond Bar’s position as a hub for sustainable industrial waste treatment and public health protection.

Wastewater Treatment Regulations: Key Industrial Waste Compliance Standards in Diamond Bar
Los Angeles County’s Regulatory Bodies and the Sewer System
Regulation of industrial waste water treatment falls under several agencies in Los Angeles County , including the Department of Public Works and regional water boards. These entities enforce standards for sewer connections, surface water protection, and disposal permit issuance for all treatment facilities in Diamond Bar. Inspection routines, permit renewals, and random water quality sampling are key enforcement methods used to ensure ongoing compliance.
Any facility found discharging waste in violation of permit terms faces rapid escalation, which may include formal citations, mandatory corrective action, and operational shutdowns if public health is at risk. This regulatory rigor maintains high standards for the sewer system and supports public trust in local water quality.
Diamond Bar’s Specific Industrial Wastewater Treatment Criteria
The City of Diamond Bar supplements county standards with additional local criteria, including limits on heavy metals, strict pH requirements, and advanced chemical monitoring. Compliance with sewer line integrity and regular maintenance of on-site pre-treatment systems are also mandated. These regulations not only protect the public sewer but help prevent long-term infrastructure degradation and water quality issues.
Enforcement, Monitoring, and Reporting Requirements
Facilities are required to implement continuous monitoring for regulated contaminants and submit regular reports to city and county agencies. Many sites now use automated sensors to track effluent quality and trigger alerts for permit violations. Annual or biannual facility inspections supplement electronic monitoring, ensuring a robust safety net that guards both public works infrastructure and local ecosystems.
Public Sewer Systems and Industrial Waste Water Treatment Diamond Bar
Integration Between Industrial Waste and the Public Sewer
Industrial wastewater treatment in Diamond Bar depends heavily on seamless integration with the public sewer system. Industrial facilities must install and maintain high-quality connections, including backflow preventers and inspection points. This integration ensures that only properly treated water makes its way into the municipal network, reducing risks of sewer system overload or accidental discharge to surface waters.
Close coordination between industry and public works helps manage large fluctuations in daily wastewater volumes, particularly during peak industrial activity. It also helps prevent cross-contamination with residential or commercial waste lines.
Challenges in Sewer Line Maintenance and Monitoring
Maintaining the integrity of the vast sewer line network is an ongoing challenge for Diamond Bar’s public works teams. Potential issues include buildup of residual sludge, corrosion from chemical-laden waste, and infiltration from aging pipes. Advanced remote monitoring and periodic physical inspections are critical to catch problems early—before they can cause costly breakdowns or permit violations.
Continuous investment in automated sensors, repair technology, and skilled labor ensures the ongoing health of the municipal wastewater system and supports sustainable growth for local industries.

Role of Septic Tanks and On-Site Wastewater Treatment in Diamond Bar
When Are Septic Tank Systems Appropriate?
While septic tank systems are rarely used by large industries in Diamond Bar, they remain a viable option for small, isolated facilities without access to the public sewer. Such systems must meet specific regulatory standards for both design and periodic maintenance, reducing environmental and health risks. Monitoring by public health agencies ensures these systems do not negatively impact underground or surface water.
Comparison: Septic vs Sewer System for Industrial WasteSeptic systems offer moderate cost and independent operation, useful in rural zones or areas with unique wastewater compositions. However, they present more operational challenges—requiring frequent inspection, limiting discharge volumes, and raising risks for permit violations if not maintained. The public sewer system , by contrast, offers greater capacity, scalability, and regulatory support, making it ideal for most industrial operations in Diamond Bar.

Advanced Industrial Waste Disposal Strategies and Best Practices
Optimizing Industrial Waste Disposal for Environmental Sustainability
Sustainable industrial waste disposal strategies prioritize pollution prevention at the source, ongoing employee training, and active collaboration with regulatory agencies. Diamond Bar industries invest in advanced filtration units, closed-loop recycling systems, and real-time monitoring software to keep their environmental impact low.
Best practices include segregating toxic compounds, reducing waste production through process modification, and using green chemicals that are less hazardous to the sewer system and public sewer environment.
Reducing Contaminants Before Public Sewer Entry
One of the smartest strategies is pre-treatment —removing contaminants before wastewater reaches the sewer line. Tools like oil separators, sedimentation tanks, and chemical neutralization beds help companies stay below permitted levels for regulated pollutants. These pre-treatment steps minimize damage to the public works infrastructure and reduce the frequency of permit violations.
Collaboration with licensed contractors ensures systems meet regulatory standards and can scale as business needs grow. Routine training for facility staff ensures processes are followed and data is properly recorded for compliance audits.
Conduct regular water quality testing and internal audits.
Invest in real-time digital monitoring and automated controls.
Maintain clear documentation for all permit renewal periods.
Collaborate with the City Council and Public Works offices for continuous improvement.
Upgrade treatment plant equipment regularly to keep up with technological advances and new regulations.
Selecting the Right Treatment System for Industrial Waste Water in Diamond Bar
Evaluating Treatment Systems: Capacity, Scalability, and Compliance
Choosing the right treatment system depends on a facility’s specific wastewater output, current and projected capacity demands, and compliance history. Decision-makers must weigh potential growth, local regulatory thresholds, and the compatibility of a facility’s waste stream with available technologies.
Working with engineering consultants and regulatory officials during the evaluation process speeds up permit approval and reduces the chances of future permit violation. Continuous investment in scalable, modular solutions prepares facilities for tighter future regulations and demand surges.
Pros and Cons of Popular Wastewater Treatment Technologies in Diamond Bar |
||
Technology |
Advantages |
Challenges |
|---|---|---|
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) |
High contaminant removal, compact footprint, automation-ready. |
Higher capital costs, periodic membrane cleaning needed. |
Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) |
Flexible operation, handles variable flows, good for upgrades. |
Labor intensive, potential for cycle disruption. |
Chemical Precipitation |
Effective for heavy metals, relatively simple to operate. |
Produces chemical sludge, disposal may be costly. |
Constructed Wetlands |
Low energy, eco-friendly, supports biodiversity. |
Space intensive, slower contaminant removal. |
Key Challenges in Industrial Waste Water Treatment Diamond Bar and How to Overcome Them
Common Issues: Sewer System Overload, Chemical Runoff, and Permit Violation
The most frequent issues for Diamond Bar industries include sewer system overload (often caused by high-volume discharges), chemical runoff from accidental spills, and permit violations due to incomplete recordkeeping or outdated equipment. Overloads can lead to backups, surface water contamination, or regulatory penalties, while unmanaged chemical runoff endangers both the environment and public health.
Strict facility maintenance, staff training, and prompt issue escalation help manage these common risks. Planning for peak usage and periodically reviewing compliance paperwork keep violations to a minimum.
Innovative Solutions: Automation, Remote Monitoring, and Advanced Filtration
Diamond Bar has embraced advanced solutions to meet these challenges—automated process controls, real-time monitoring platforms, and smart filtration units that detect contaminant spikes before they exit the facility. These investments enable rapid response to emerging problems, improve water quality outcomes, and streamline compliance reporting.
Ongoing collaboration with technology vendors and regional public works agencies keeps solutions current and ensures the city adapts quickly to new or evolving threats to the sewer system and surface waters.

Cost Analysis: Investing in Industrial Waste Water Treatment Diamond Bar
Breakdown of Typical Costs: Equipment, Permits, Maintenance
An effective industrial waste water treatment strategy requires investment in equipment (pumps, tanks, sensors), acquisition and annual renewal of disposal permits , and ongoing maintenance for both physical and digital assets. Equipment costs vary with plant size but can range from $150,000–$5 million, while annual permit and compliance costs typically run between $1,000–$25,000. Scheduled maintenance and rapid-response repairs help avoid unexpected fines or downtime.
Calculating Return on Investment for Upgrading Treatment Plants
Upgrading to advanced treatment technologies may seem expensive at first, but the long-term return on investment is significant. Facilities benefit from fewer permit violations, lower energy and chemical use, reduced labor costs through automation, and stronger community and regulatory relationships.
Companies that modernize treatment systems are also more resilient against future regulatory changes and enjoy better insurance terms—making them better positioned for safe, profitable, and sustainable growth.
Projected Annual Operating Costs for Diamond Bar Wastewater Treatment Systems |
|||
System Type |
Annual Operating Cost |
Typical Maintenance Cost |
Compliance/Permit Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
Centralized (Shared) |
$75,000–$250,000 |
$12,000–$40,000 |
$5,000–$10,000 |
Decentralized (Private) |
$30,000–$120,000 |
$6,000–$20,000 |
$2,000–$6,000 |
On-Site (Small Facility) |
$8,000–$25,000 |
$1,000–$4,000 |
$1,000–$2,000 |
Environmental Impact: How Effective Industrial Waste Water Treatment Benefits Diamond Bar and Beyond
Mitigating Industrial Pollution in Los Angeles
Effective industrial waste water treatment is the region’s first and best defense against pollution. By removing harmful chemicals, metals, and organic waste, Diamond Bar’s facilities reduce the volume and toxicity of industrial waste entering Los Angeles County’s sewer and water systems, protecting fragile surface waters and helping to keep public waterways safe.
Protecting Local Waterways and Ecosystems
Reducing pollutant loads to surface water directly benefits local rivers, creeks, and wetland ecosystems. Healthier aquatic habitats support robust biodiversity, enhance recreational opportunities, and maintain the beauty and vitality of Diamond Bar’s natural environment.
Community Health Improvements from Robust Water Treatment
Improvements in water quality translate to healthier communities. By limiting pollution and enforcing strict monitoring, Diamond Bar ensures that residents have access to cleaner surface and groundwater, while workers and families enjoy safer workplaces and neighborhoods. Community health is lifted by each step in the water treatment journey, reinforcing public support for ongoing investment.

Case Studies: Successful Industrial Waste Water Treatment in Diamond Bar
Real-World Example: Upgrading Sewer Lines and Treatment Plants
A recent upgrade at a major Diamond Bar manufacturing plant involved replacing old sewer lines and installing a new membrane bioreactor treatment system. The investment reduced contaminant output by 85%, enabled the company to process 50% more wastewater without exceeding limits, and resulted in a reduction of permit violations from four per year to zero.
Lessons Learned from Innovative Waste Disposal Solutions
The most successful projects involve close partnership between industry, city officials, and technology vendors. “Lessons learned” include the value of investing in staff training, using digital tools to spot issues early, and keeping an open line with public works for regulatory updates and emergency responses. Proactive companies also continually monitor emerging technologies and update systems to maintain a competitive—and compliant—edge.
Industrial Waste Water Treatment Diamond Bar: Maintenance, Monitoring, and Optimization
Routine Maintenance for Treatment Systems
Regular inspections, pump and filter replacements, and cleaning of pipes and holding tanks are the foundation of reliable operations. Diamond Bar industries follow strict schedules to avoid backlog, system slowdowns, or safety hazards. Documentation of each maintenance activity is essential for passing regulatory reviews and permit renewals.
Utilizing Data and Remote Sensing for Process Optimization
Modern control rooms now aggregate vast amounts of real-time data—from effluent quality to equipment condition. Advanced analytics and remote sensors catch deviations fast, alerting operators before contaminants can reach the public sewer or surface water. Using these tools optimizes chemical use, reduces downtime, and improves environmental outcomes.
Emergency Protocols for Waste Water Incidents
Despite best efforts, incidents—like major spills or system failures—do occur. Diamond Bar mandates rapid notification of city officials and swift deployment of containment or neutralization measures. Drills and emergency planning ensure staff are prepared, minimizing risk to the environment and public.
Future Innovations in Industrial Waste Water Treatment for Diamond Bar
Emerging Filtration and Treatment Plant Technologies
Emerging trends include enhanced biological reactors, nanofiltration, and next-gen digital platforms. These systems promise lower energy consumption, higher contaminant capture, and greater ease of integration with Diamond Bar’s other sustainability initiatives. The city’s strong tradition of innovation all but guarantees rapid deployment of next-generation solutions.
Policy Trends: Anticipated Changes in Waste Water Regulations
State and county policies will likely tighten maximum contaminant levels, require higher frequency of inspections, and increase reporting transparency. Facilities with flexible, adaptive treatment systems will be best positioned to handle these shifts, avoiding costly retrofits and operational slowdowns.
Preparing Diamond Bar Enterprises for a Sustainable Future
Business leaders in Diamond Bar should embrace a culture of continuous improvement. Ongoing staff education, technology upgrades, and transparent engagement with public works departments will keep local industries competitive and compliant—helping to protect Diamond Bar’s environment and economic vitality for decades to come.
People Also Ask About Industrial Waste Water Treatment Diamond Bar
What is the process of obtaining an industrial waste disposal permit in Diamond Bar?
Start with a pre-application meeting with the environmental compliance division.
Complete and submit the formal permit application with supporting technical documentation and an operations plan.
Participate in a mandatory site visit and water quality assessment.
Address any deficiencies flagged by city staff and provide clarifications as needed.
Receive permit approval following successful review and begin (or continue) discharge operations.
How does Diamond Bar's industrial waste water treatment compare to national best practices?
Diamond Bar’s systems align with—and sometimes exceed—national benchmarks for contaminant removal, automation, and reporting.
The city regularly updates technology and protocols to remain at the forefront of water quality protection.
Ongoing collaboration with Los Angeles County yields strong integration between local and federal standards.
Are advanced treatment systems required for all industries in Diamond Bar?
Most large-scale industries must use advanced or specialized treatment systems to meet strict permit requirements.
Small, low-risk operations may use basic filtration or approved septic systems, but are still subject to routine audits.
Industry category and discharge profile determine the minimum required technology for compliance.
How frequently must treatment plants be inspected or upgraded in Diamond Bar?
Inspections occur at least annually, with increased frequency for high-risk or large-scale sites.
Upgrades are triggered by permit renewal cycles, regulatory changes, or when operational deficiencies are discovered.
Ongoing preventive maintenance helps facilities avoid emergency retrofits and unexpected downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions on Industrial Waste Water Treatment Diamond Bar
How does industrial waste water enter the sewer system?
Through pre-treated drains and approved sewer connections, industrial wastewater is routed into Diamond Bar’s public sewer system for further treatment.What are the penalties for failing to comply with wastewater treatment regulations in Los Angeles County?
Fines can range from several thousand to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the infraction. Repeated violations can lead to permit revocation or facility closure.Who oversees wastewater treatment and public sewer maintenance in Diamond Bar?
Oversight is a joint effort between the Diamond Bar Public Works Department, Los Angeles County Water Board, and environmental regulators.Can small businesses use septic tanks for industrial wastewater disposal?
Only if the business meets strict design, monitoring, and approval criteria—most are connected to the public sewer for compliance and safety reasons.
How to Get Started: Implementing Industrial Waste Water Treatment in Diamond Bar
Follow the checklist for new facilities or operators: review regulations, assess waste profiles, plan for pre-treatment and main treatment phases, and apply early for permits.
Choose among Diamond Bar’s approved treatment plants or work with licensed contractors for design, installation, and ongoing maintenance.
Leverage city and county resources for ongoing education and stay ahead of compliance changes—subscribe to official newsletters and attend public information sessions.
Key Takeaways: What Every Industry in Diamond Bar Should Know About Waste Water Treatment
Investing in advanced waste water treatment safeguards local ecosystems for future generations.
Compliance with disposal permits is mandatory under Los Angeles County law and helps prevent costly violations.
Adopting best practices in waste water treatment improves both operational efficiency and community health.
Taking Action: Connect With Industrial Waste Water Treatment Diamond Bar Experts Today
Ready to take your industrial waste management to the next level? Schedule a consultation or site visit with certified Diamond Bar experts for custom solutions.
Download our free guide or access checklists for compliance, system optimization, and emergency preparedness.
Have feedback or need ongoing support? Get in touch to help drive continuous environmental improvement in Diamond Bar and beyond.
Take concrete steps today—contact a licensed expert, upgrade your systems, and invest in the future of Diamond Bar’s water and community!
Sources
Los Angeles County Department of Public Works – https://dpw.lacounty.gov/
California State Water Resources Control Board – https://www.waterboards.ca.gov/
United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) – https://www.epa.gov/
For a comprehensive understanding of industrial wastewater treatment in Diamond Bar, consider exploring the following resources:
“Diamond Bar, California Hazardous Waste Management Services” : This resource provides insights into hazardous waste management practices in Diamond Bar, detailing services such as chemical disposal, emergency spill response, and hazardous waste management. ( usahazmat.com )
“Adopted Orders/Permits | Los Angeles Regional Water Quality Control Board” : This page offers information on permits and orders related to wastewater discharge in Diamond Bar, including details about the city’s compliance with statewide general waste discharge requirements. ( waterboards.ca.gov )
These resources will provide valuable insights into the regulatory frameworks and services available for effective industrial wastewater management in Diamond Bar.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment